The following guidelines provide information about the responsibilities of a test reader. If you have any questions about a specific test, please contact Disability Services.
Disabilities and Health-related Needs
Select an option below for more information
The following guidelines provide information about the responsibilities of a test reader. If you have any questions about a specific test, please contact Disability Services.
A test taker is permitted to ask the reader to write notes and to assist with intermediate steps in computing mathematics problems, especially if the test taker has no tools or equipment for taking notes or is unable to do so. For example, in the multiplication of numbers (e.g., 17 x 521), a test taker may say, "Seven times one is seven. Put down the seven. Seven twos are fourteen. Put down the four to the left of the seven and carry the one." The test taker should be specific in directions to the reader as to what they write, in which column to write it, what to carry, etc.
Mathematical expressions must be read precisely and with care to avoid misrepresentation for a test taker who has no visual reference. For math items involving algebraic expressions or other mathematical notation, it may be preferable for the reader to silently read the entire question before reading it aloud to the test taker. Use technically correct yet simple terms and be consistent in the treatment of similar expressions. Some typical expressions and the manner in which they should be read follow:
(a) Lowercase letters that are juxtaposed should be read as a multiplication expression: e.g.,
xy should be read as "x y," unless it is part of a complex expression or this reading is otherwise unclear, in which case read it as "x times y."
(b) Capital and lowercase letters should be differentiated because they can have different meanings in mathematical or scientific expressions.
e.g., R - 2y = 6 should be read as "Capital R minus two y equals six."
(c) Simple numerical fractions should be read as fractions: e.g.,
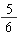 should be read as "five sixths."
should be read as "five sixths."
However, similar letter expressions can be read as one letter "over" another: e.g.,
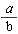 should be read as "a over b."
should be read as "a over b."
(d) To prevent confusion, complicated fractions (those that contain other mathematical operations) should be read in terms of their numerators and denominators: e.g.,
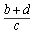 should be read as "a fraction with numerator b plus d and denominator c."
should be read as "a fraction with numerator b plus d and denominator c."
If there is any question as to where the fraction ends, say "end fraction."
(e) Negative numbers should be read as "negative."
e.g., -5 should be read as "negative five," not "minus five."
When a subtraction operation is involved, read the sign as "minus," e.g.,
x - 5 should be read as "x minus five."
(f) Expressions containing multiple mathematical operations should be read exactly as they appear. Expressions containing parentheses or brackets can be read in any of the following three ways:
quantity, close quantity
paren, close paren (or bracket, close bracket)
left paren, right paren (or left bracket, right bracket)
For "paren, close paren" or "left paren, right paren," it is also acceptable to use "parenthesis" instead of "paren." If you use the term "quantity," in complicated expressions, announce where enclosed portions end by saying "end quantity."
e.g., (2x - 6y) - 10 could be read
as "The quantity two x minus six y, close quantity, minus ten;"
as "paren, two x minus six y, close paren, minus ten;"
or as "left paren, two x minus six y, right paren, minus ten."
a (x - y) could be read as "a, parenthesis, x minus y, close parenthesis."
a × b2 could be read as "a times the square of b."
Use pauses to audibly group sections of an expression together.
z + (-a) could be read as "z plus [PAUSE] paren negative a close paren."
(g) If equations are used in the test you will be reading:
Since equations are a shorthand means of stating relationships between quantities, the reader's job is to translate this shorthand back into everyday English. Read equations in this order:
If the equation is numbered, read its number first.
Give the meaning of each letter or symbol.
Read the equation.
e.g.,
Eq. 6-2
E = mc2 |
E = energy in ergs |
|
m = mass in grams |
|
c = speed of light in cm./sec. |
Read as "Equation six dash two. Capital E equals energy in ergs, m equals mass in grams and c equals the speed of light in centimeters per second. Then, Capital E equals m c squared."
An approved reader should be admitted to the test center with the test taker. The reader's photo-bearing identification should be checked.
Prior to the start of the exam, the test center administrator/supervisor will review the Guidelines with the test taker and the reader and will set the ground rules for the conduct of the examination.
The test administrator must remain in attendance at all times during the test administration.
An approved reader is not present to function as an aide to the test center staff. It is inappropriate to ask the reader to perform clerical duties of any kind. The reader should not be asked to assume any responsibilities belonging to either the center staff or the test taker.
Test center staff must ensure that proper test security is maintained at all times. It’s important that the test administrator ask questions and avoid any hasty interpretations of what may be communication of test content or exchange of information between the test taker and the reader that might give the test taker an unfair advantage. The task requested by the test taker might be acceptable once understood. Discussion or communication concerning interpretation of test content is not permitted. If such discussion occurs and can’t be controlled, or if test center staff observe anything they deem unusual, the situation should be reported on the Supervisor's Irregularity Report (SIR) or the Electronic Irregularity Report (EIR) and the test taker advised of this action.
The test center administrator may also stop the test and dismiss the test taker if they believe that the reader has provided the test taker with any unfair advantage. In such instances, ETS reserves the right to cancel the test taker's score.